Explore and learn more about Rolling deployment, when to use this strategy, its advantages and how teams can perform rolling deployments with BuildPiper, here in this blog!
What is Rolling Deployment?
A Rolling deployment is a deployment strategy in Kubernetes. It replaces the existing pods in a cluster with a new version, updating pods slowly one by one, without cluster downtime. The rolling update does readiness checks to examine if a new pod is ready before starting to scale down existing pods with the old version. If there is an issue, users can stop an update and roll it back, without stopping the entire cluster.
When to use Ramped/Rolling Deployment?
Ramped/Rolling Deployment- best for SLOW ROLLOUTS!
- When you want to take zero downtime during an application update.
- When your application supports having old code and new code running at the same time.
- When you’re releasing to development/staging/production environments.
Implementation of Rolling Deployment Strategy!
A rolling update deployment strategy is a deployment strategy where the applications are gradually deployed one at a time or in batches. This Kubernetes deployment strategy slowly replaces previous versions of an application with new versions of an application by completely replacing the infrastructure on which the application is running.
In the rolling update deployment strategy, the old and new versions remain in a live state at the same time until the new version completely replaces the old version. There would be a need of executing at least N+1 instances of the application in order to implement a rolling deployment. The additional node would be required to run the new version of the application.
Once the instance of the new version is released, its performance and its error rate are checked and monitored. If the new version passes all the necessary health checks, then another instance is pushed into production and monitored. This process repeats itself in an iterative manner until the new version is the only version up and running.
Advantages of Rolling Deployment Strategy!
The benefits of a rolling update deployment strategy include,
- There is minimal downtime as current versions stay in the live state.
- Requires only one additional node instead of an entire duplicated infrastructure like that in the blue-green deployment strategy.
- It is possible to return all traffic to the previous version if there is a need for rollback.
Rolling Deployment with BuildPiper!
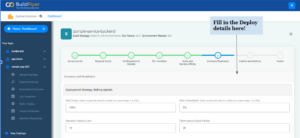
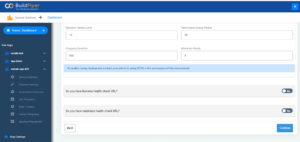
Here’s how you can deploy a Microservice with BuildPiper using the Rolling Deployment strategy. By default, BuildPiper uses the Rolling deployment strategy for deploying services. All you need to do is follow these simple steps,
- Sign in to the BuildPiper user portal.
- Choose the service that you need to deploy.
- Submit the deployment configuration details.
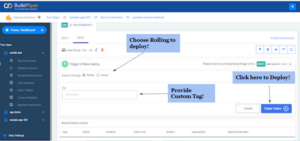
- Select the custom tag.
- Choose “Rolling” if you want to deploy using the Rolling deployment strategy.
- Finally, trigger the deployment by clicking on the “Trigger Deploy” button.
Explore more about this powerful Microservices & Kubernetes Delivery platform to know its other interesting features and how it can empower teams with a seamless and secure Kubernetes deployment! Contact us NOW!